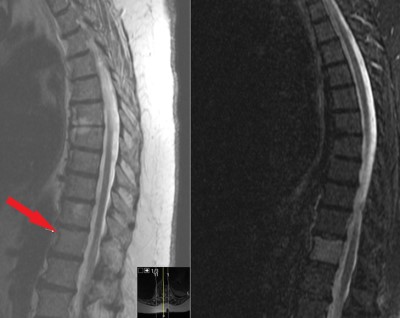
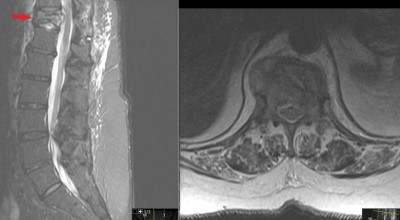
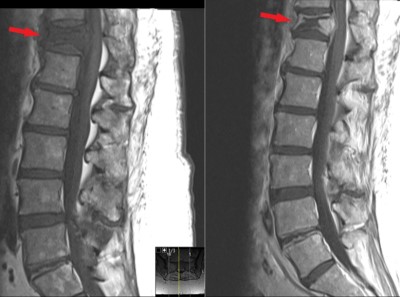
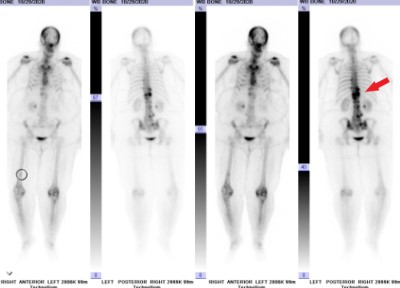
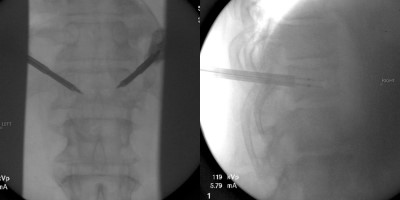
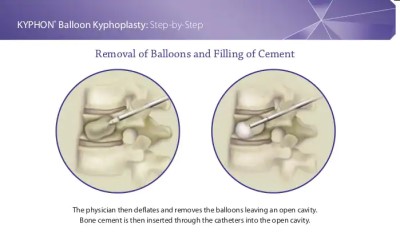
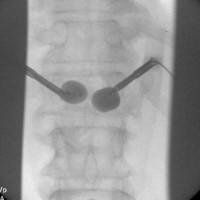
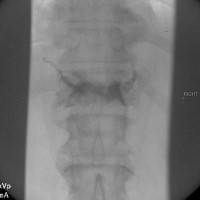
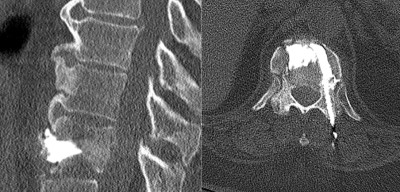
This is a 66 year old female who presents with severe back pain.
She has known history of breast cancer with spread to multiple bones.
Back pain started 8 weeks prior without specific traumatic event.
No neurologic complaint.
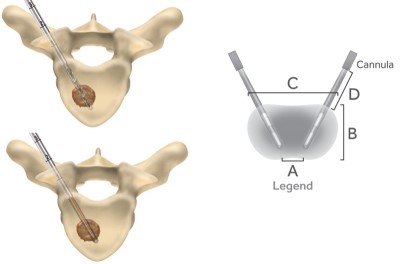
Diagrams demonstrating the transpedicular approach to the lesion. First, a drill is advanced into the vertebral body (top left), then a radio-frequency (RF) electrode is placed into the lesion (bottom left). When RF energy is applied an area around & between the electrodes is ablated (grey area on right image). [Courtesy of Medtronic OsteoCool]
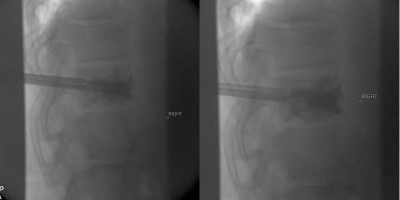
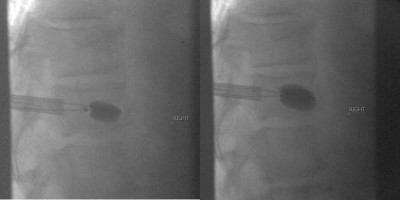
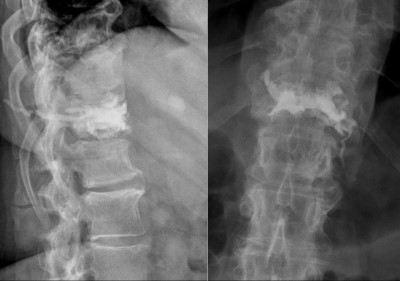
Intraoperative fluoroscopic (x-ray) images showing the injection of the kyphoplasty cement (methyl methacrylate) in the lateral plane. The left image shows a partial injection with the injection needles in place. The right image demonstrates the cement seen after full injection after the filling needles have been removed; access needles remain in place.
- All
- Pre-Op
- Intra-op
- Post-op